The Truth About Medical Cannabis l Therapureoil
The Truth About Medical Cannabis: Exploring Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids
Cannabis has a long history as a medicinal plant, dating back thousands of years. Ancient cultures in China, Israel, Egypt, and many other regions documented its use to treat a variety of ailments, including pain, nausea, and anxiety. Although there were no clinical trials at that time, historical records indicate its therapeutic benefits were well recognized.
However, since the late 1960s, cannabis has been classified as a controlled substance, grouped in the same category as heroin and cocaine in many countries. This classification significantly restricted clinical research and medical use, creating barriers to fully understanding its potential health benefits.
What Is the Cannabis Family Made Of?
The cannabis plant is broadly divided into two main varieties: hemp and marijuana. Each variety contains a vast range of cultivars (strains), chemotypes (chemical profiles), and chemovars (chemical variations). In fact, cannabis flowers contain over 500 active compounds, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, all of which contribute to the plant's unique therapeutic properties.
The Effects of Cannabinoids: Beyond THC and CBD
Most people are familiar with delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the compound responsible for the "high" associated with marijuana use. On the other hand, Cannabidiol (CBD) has gained popularity in the wellness world for its non-psychoactive properties and potential health benefits.
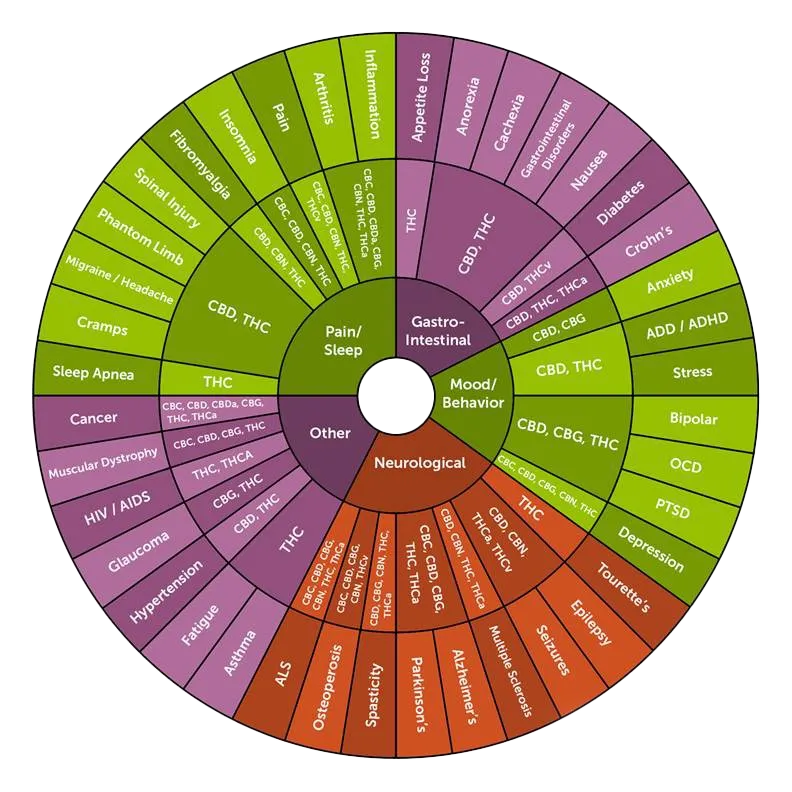
But THC and CBD are just two of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis. Other notable cannabinoids, such as CBG(cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol), and CBC (cannabichromene), also exhibit various biological effects without the intoxicating effects associated with THC. These cannabinoids interact with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a role in maintaining balance and supporting overall health.
Cannabinoids and they’re properties
Why the Entourage Effect Matters
One key aspect of cannabis medicine is the entourage effect, a phenomenon where the plant's various compounds—cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids—work together synergistically to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This means that consuming a full-spectrum cannabis extract may be more effective for some health conditions than using isolated compounds.
Cannabis Classification and the Challenges of Research
Despite its history and the growing body of anecdotal evidence, the classification of cannabis as a controlled substance has significantly hindered research. This classification not only limited access to the plant for medical purposes but also stunted the exploration of its therapeutic potential through clinical trials.
Today, with changing regulations and a shift in public perception, more scientific studies are being conducted to explore the true potential of cannabis for medical use. Researchers are delving deeper into the roles of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, seeking to understand how these compounds can address conditions like chronic pain, inflammation, anxiety, and neurological disorders.
The Takeaway
The cannabis plant is complex, with numerous chemical compounds that contribute to its effects. Understanding the differences between THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids, as well as the role of the entourage effect, is key to unlocking its medicinal potential. With increased research and evolving laws, we are just beginning to uncover the therapeutic benefits that ancient cultures seemed to know all along.
Unlocking the True Potential of Medical Cannabis: Understanding the Entourage Effect
Cannabis has been used medicinally for thousands of years, with ancient cultures in China, Israel, and Egypt documenting its benefits for conditions like pain, nausea, and anxiety . Despite its long history, the classification of cannabis as a controlled substance since the late 1960s has limited clinical research into its therapeutic potential. However, as regulations evolve, more is being discovered about the full benefits of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids found in the cannabis plant.
The Power of the Entourage Effect
The entourage effect refers to the synergistic interaction of the plant’s various compounds, including cannabinoids(such as CBD and THC), terpenes, and flavonoids, which work together to amplify therapeutic effects. Unlike modern pharmaceuticals, which often isolate a single compound, cannabis-based therapies are more effective when the full range of natural components is utilized . This holistic approach is also seen in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), where multiple herbs are combined to achieve the best therapeutic results.
What Makes Cannabis Truly Medicinal?
The cannabis family is composed of hemp and marijuana, each containing a variety of cultivars, chemotypes, and chemovars. The plant itself holds over 500 active compounds, many of which contribute to its healing properties . The most well-known cannabinoids, THC and CBD, are just the tip of the iceberg. Other cannabinoids like CBG, CBN, and CBC exhibit various biological effects without the intoxicating properties of THC .
Terpenes and Flavonoids: More Than Aromas
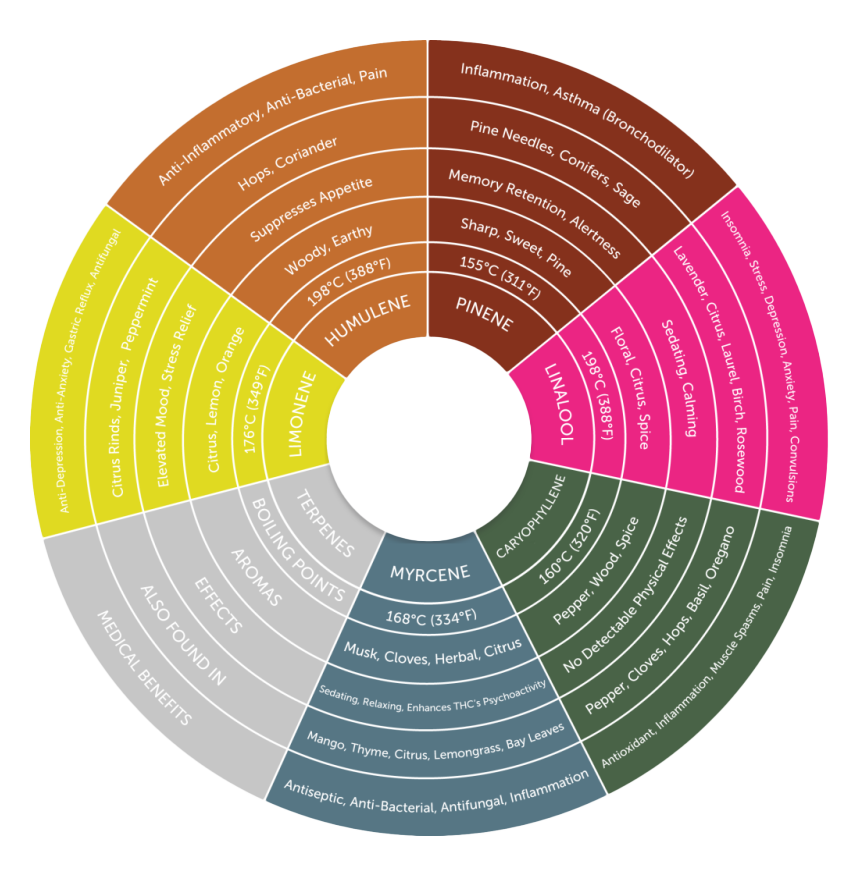
Beyond cannabinoids, cannabis is rich in terpenes and flavonoids, which also play a role in the plant’s therapeutic effects. These compounds are not unique to cannabis and are found in many other plants, fruits, and vegetables. Terpenes, for example, are the foundation of aromatherapy and contribute to the plant's distinct scent. They offer benefits such as promoting sleep, stimulating appetite, alleviating anxiety, and reducing inflammation . When combined with cannabinoids, they enhance the overall therapeutic experience.
Terpenes and their Physio-Biochemical effect on our metabolism
Why Full-Spectrum Cannabis Oil Is Superior
A full-spectrum cannabis oil harnesses the complete range of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, maximizing the therapeutic effects through the entourage effect. In contrast, many commercially available cannabis oils are made using isolates, such as pure CBD or THC, which lack these additional beneficial compounds. As a result, these oils may be less effective for conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation, requiring higher doses to achieve similar results .
To ensure the quality and therapeutic efficacy of a cannabis oil, it's important to request a Certificate of Analysis from the supplier. One quick way to check the quality is through the smell test: a full-spectrum oil should have a noticeable aroma due to the presence of terpenes. An odorless oil is likely an isolate in a carrier oil, offering fewer therapeutic benefits.
Methods of Using Medical Cannabis
There are several ways to use medical cannabis, each with different benefits:
Smoking: While effective, smoking is not recommended due to lung health concerns.
Vaping Dry Herbs: Provides rapid relief with effects lasting around 2 hours and is considered less harmful than smoking.
Cannabis Oils: Taken orally, they offer longer-lasting effects (6 to 12 hours) and are ideal for ongoing symptom management.
Nasal Sprays: Some pharmaceutical products contain a 1:1 ratio of THC and CBD, though these can be expensive.
The Importance of High-Quality Extraction: Therapureoil’s Approach
Not all cannabis oils are created equal. Many products on the market are labeled as “organic” but still lack the full-spectrum of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. This is often due to extraction methods that prioritize cost and efficiency over therapeutic value.
Therapureoil sets itself apart with its proprietary organic solventless extraction technology, which retains the full range of active compounds. This ensures that each product delivers the complete therapeutic benefits of the cannabis flower, maximizing the entourage effect. Therapureoil's full-spectrum formulations are crafted using carefully selected cultivars and chemovars to address specific health needs, such as inflammation, pain relief, anxiety, and overall wellness .
Choosing the Right Medical Cannabis Oil
For those looking to use medical cannabis, it's essential to select products that offer true full-spectrum benefits:
Verify the Oil's Composition: Look for oils that include not only CBD and THC but also other cannabinoids and terpenes.
Ask for the Certificate of Analysis: This will confirm the presence of various compounds and the absence of contaminants.
Smell the Oil: If it smells like cannabis, it likely contains the beneficial terpenes needed for the entourage effect.
The Difference Between Medical and Recreational Cannabis
While recreational cannabis may be used for enjoyment, it does not always meet the rigorous standards required for therapeutic use. Medical cannabis, like any other medication, should be chosen carefully to ensure the best results.
At Therapureoil, we educate and guide patients on selecting the most suitable products for their needs, considering factors such as the desired effects, method of use, and individual health conditions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Full Potential of Medical Cannabis
The entourage effect in cannabis therapy is not just a concept but a proven approach that amplifies the therapeutic benefits of the plant’s natural compounds. By choosing full-spectrum cannabis oils extracted through advanced methods like Therapureoil's proprietary technology, patients can experience more effective relief from conditions such as chronic pain, inflammation, and anxiety.
As the world of medical cannabis continues to evolve, understanding the roles of cannabinoids, terpenes, and the entourage effect will be key to unlocking the plant's full healing potential.
References
Russo, E. B. (2007). History of cannabis and its preparations in saga, science, and sobriquet. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 4(8), 1614-1648.
Russo, E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology, 163(7), 1344-1364.
McPartland, J. M., & Russo, E. B. (2001). Cannabis and cannabis extracts: Greater than the sum of their parts? Journal of Cannabis Therapeutics, 1(3-4), 103-132.
ElSohly, M. A., & Slade, D. (2005). Chemical constituents of marijuana: The complex mixture of natural cannabinoids. Life Sciences, 78(5), 539-548.
Cascio, M. G., & Pertwee, R. G. (2014). Known pharmacological actions of nine non-psychotropic phytocannabinoids. Handbook of Cannabis, 137-156.
Baron, E. P. (2018). Medicinal properties of terpenes found in cannabis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(4), 50.
Aizpurua-Olaizola, O., et al. (2016). Evolution of the cannabinoid and terpene content during the growth of cannabis sativa plants from different chemotypes. Journal of Natural Products, 79(2), 324-331.
Abrams, D. I., & Guzman, M. (2015). Cannabis in cancer care. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 97(6), 575-586.
Hanuš, L. O., & Táborský, P. (2001). Extraction of cannabinoids. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants-Industrial Profiles, 42, 71-94.